Permaculture in Malawi

In Malawi, as in any location, it is important to include the local context, resources and challenges when developing and implementing permaculture designs.
In typical permaculture practice intensive vegetable cultivation (zone 1) is planned near the house along with other resources that need attention and are used daily; however, in Malawian villages water access is often see to be problematic so traditionally, most people use a “dimba” or river floodplain away from the house for vegetable cultivation. Since these areas have sufficient water and are away from free ranging animals that destroy vegetable crops, it can be an appropriate, culturally relevant location for zone 1. But, we also work to show homes, schools, offices, restaurants and others interested in sustainable designs that there IS a lot of water around us that is often missed that can be put to great use around the zone 0 structures.
Food forests (zone 2) incorporate more trees and perennial species into the system, which tend to be heartier and more drought resistant. For this reason, zone 2 can be more applicable near the house where little water is available most of the year and free-range animals are often a problem. In the food forest, families can compost household and animal wastes to improve soil fertility and plant growth. Once established, this area can produce food year round using very little water.
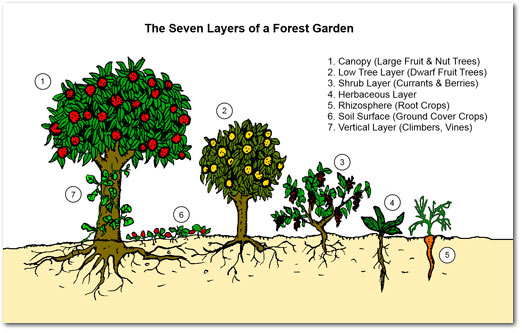
The vast majority of Malawians cultivate staple crops, which fall into zone 3. By incorporating agroecology techniques, such as crop rotation, interplanting, green manures and water management, farmers can produce staple crops while protecting the soil resource and reducing their reliance on expensive inputs. By increasing soil health and improving water management, these practices can also safeguard against extreme weather events and periods of drought.
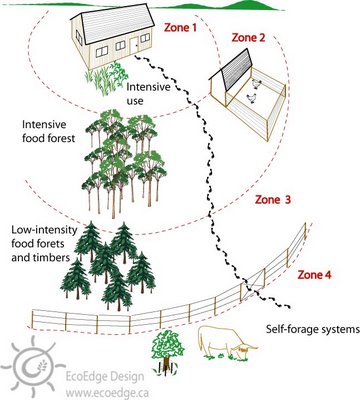
While most households in Malawi have access to and control over zones 1, 2 and 3, zones 4 and 5 tend to either be communal areas or do not exist. In a country with extreme levels of deforestation and forest degradation, efforts to build sustainable, managed forests and natural areas are crucial.

